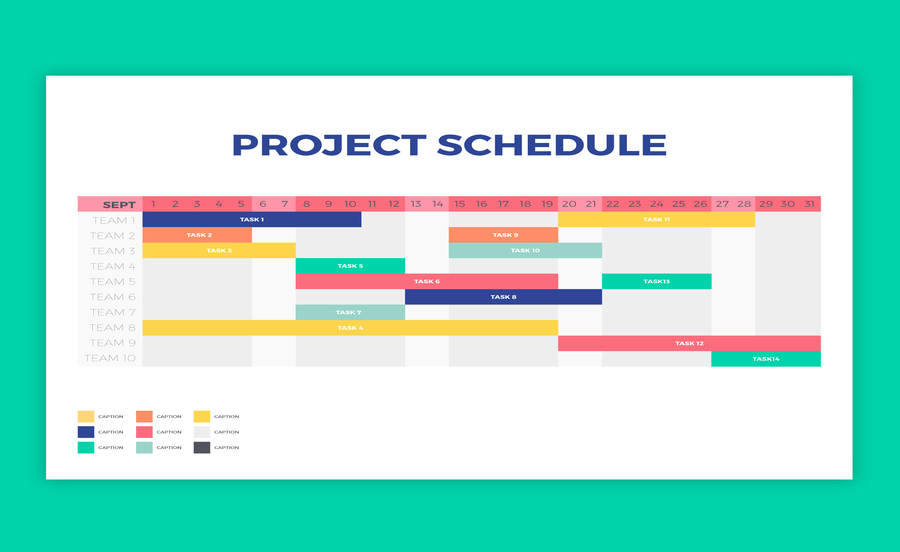
In the realm of project management, the Gantt chart stands as a quintessential tool for visualizing tasks, timelines, and dependencies. Within this dynamic landscape, the concept of a roadmap emerges as a pivotal element, guiding project teams towards successful execution and delivery. In this blog, we delve into the intricacies of roadmaps within Gantt charts, offering a comprehensive understanding of their significance, components, and application in modern project management practices.
Introduction to Gantt Charts
Before delving into roadmaps, let’s first establish a foundational understanding of Gantt charts. Developed by Henry Gantt in the early 20th century, Gantt charts provide a visual representation of project schedules, tasks, and timelines. By depicting tasks as bars along a timeline, Gantt charts enable project managers to plan, schedule, and track progress with precision and clarity.
The Essence of Roadmaps
In the context of Gantt charts, a roadmap serves as a strategic plan outlining the trajectory of a project over time. Unlike traditional Gantt charts that focus on specific tasks and their durations, roadmaps provide a broader perspective, highlighting key milestones, deliverables, and overarching objectives. Essentially, roadmaps offer a high-level view of the project’s journey from initiation to completion, guiding stakeholders towards a shared vision of success.
Components of a Roadmap
A comprehensive roadmap within a Gantt chart typically comprises several key components, each contributing to its efficacy in project management:
- Milestones: Milestones represent significant events or achievements within the project timeline. These may include project kick-off, major deliverables, client reviews, or product launches. By delineating milestones, roadmaps establish clear points of progress and achievement, serving as markers of success along the project journey.
- Phases or Stages: Roadmaps often delineate project phases or stages, dividing the project lifecycle into distinct segments. These phases may align with key milestones or represent logical stages of development, such as planning, execution, testing, and deployment. By delineating phases, roadmaps provide structure and clarity, guiding teams through the sequential progression of the project.
- Dependencies: Dependencies highlight the interrelationship between tasks and activities within the project. Roadmaps may depict dependencies to illustrate the sequential order of tasks or identify critical path activities that impact project duration. By visualizing dependencies, roadmaps facilitate effective resource allocation, risk mitigation, and task prioritization.
- Resource Allocation: Roadmaps may incorporate resource allocation to delineate the allocation of human, financial, or material resources throughout the project lifecycle. By aligning resource allocation with project milestones and deliverables, roadmaps ensure optimal resource utilization and mitigate potential bottlenecks or resource constraints.
- Timeline: The timeline serves as the backbone of the roadmap, providing a chronological framework for project activities and events. Roadmaps typically display timelines along the horizontal axis, with milestones, phases, and tasks plotted along the timeline to depict their temporal progression. By visualizing timelines, roadmaps enable stakeholders to assess project progress, identify potential delays, and adjust plans accordingly.
Applications of Roadmaps in Project Management
Roadmaps play a pivotal role in project management across diverse industries and domains. Some key applications of roadmaps within Gantt charts include:
- Strategic Planning: Roadmaps facilitate strategic planning by outlining the long-term vision, goals, and objectives of the project. By aligning project activities with strategic priorities, roadmaps ensure cohesive and purposeful execution, driving organizational success.
- Stakeholder Communication: Roadmaps serve as a communication tool for engaging stakeholders and fostering alignment around project objectives and timelines. Whether presenting to executive leadership, clients, or team members, roadmaps provide a concise and visually compelling overview of the project trajectory, fostering transparency and buy-in.
- Risk Management: Roadmaps aid in risk management by identifying potential bottlenecks, dependencies, and critical path activities that may impact project timelines and deliverables. By visualizing dependencies and resource allocation, roadmaps enable project managers to proactively mitigate risks, allocate resources strategically, and maintain project momentum.
- Iterative Planning: Roadmaps support iterative planning by enabling project teams to adapt and refine project plans in response to changing requirements, priorities, or external factors. Whether incorporating feedback from stakeholders or adjusting timelines in light of emerging risks, roadmaps provide a flexible framework for iterative planning and continuous improvement.
- Performance Tracking: Roadmaps facilitate performance tracking by providing a visual representation of project progress against predefined milestones and timelines. By comparing actual progress with planned milestones, roadmaps enable project managers to assess project health, identify variances, and take corrective action as needed to ensure project success.
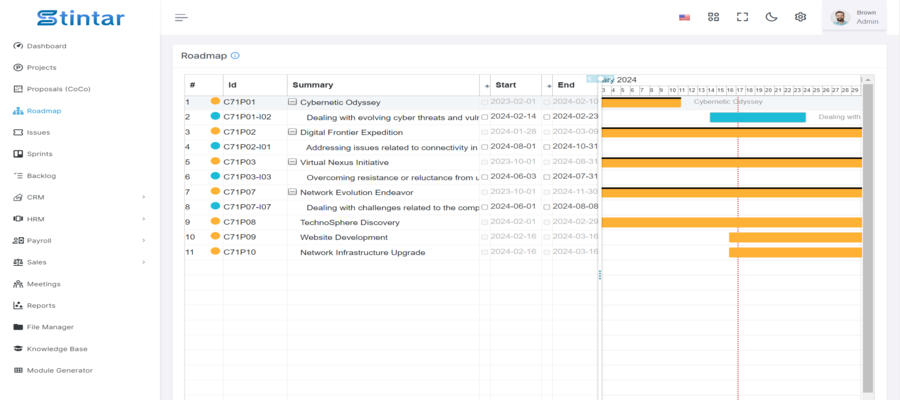
Roadmap View in Stintar
Stintar is an innovative project management platform that leverages advanced features to streamline project planning and execution. One of its standout features is its integration of roadmaps within the Gantt chart interface. Let’s explore how Stintar utilizes roadmaps to enhance project management:
- Visual Roadmap Creation: Stintar allows users to create visually appealing roadmaps directly within the Gantt chart interface. Users can easily add project objectives, milestones, and timelines, providing stakeholders with a clear overview of the project’s trajectory.
- Real-time Collaboration: Stintar facilitates real-time collaboration among team members, enabling seamless communication and updates to the roadmap. Stakeholders can access the roadmap from anywhere, ensuring everyone remains on the same page.
- Integration with Task Management: Stintar seamlessly integrates roadmaps with task management functionalities, allowing users to link roadmap milestones to specific tasks. This ensures alignment between strategic objectives and day-to-day activities, enhancing project execution efficiency.
Advanced Analytics: Stintar provides advanced analytics and reporting features to track project progress, identify bottlenecks, and optimize resource allocation. Users can generate custom reports based on roadmap data, facilitating data-driven decision making.
Conclusion
In conclusion, roadmaps are indispensable tools within Gantt charts for strategic project planning and communication. By providing stakeholders with a high-level overview of project objectives, timelines, and milestones, roadmaps ensure alignment, facilitate decision making, and mitigate risks. With innovative platforms like Stintar integrating roadmaps into project management workflows, organizations can enhance their project planning and execution capabilities, driving success in an increasingly competitive landscape.

